
 GitBucket
GitBucket
FileSystemStore in Mbed OS
- FileSystemStore in Mbed OS
- Introduction
- System architecture and high-level design
- Detailed design
- Usage scenarios and examples
- Other information
Revision history
| Revision | Date | Authors | Mbed OS version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 20 September 2018 | David Saada (@davidsaada) | 5.11+ | Initial revision |
Introduction
Overview and background
FileSystemStore is a lightweight implementation of the KVStore interface over file systems.
Requirements and assumptions
FileSystemStore assumes the underlying file system qualities for resilience and file validation. This means that if the underlying file system has no protection against power failures, then neither would FileSystemStore have.
When initializing this class, it is assumed that the underlying FileSystem is initialized and mounted.
System architecture and high-level design
Design basics
FileSystemStore implements the get/set interface using files, where a single file represents each key. A key is represented by the file name, and its value is stored as file data. Therefore, FileSystemStore imitates the get/set actions using simple file operations. Set is achieved using open-write-close, get using open-read-close and so on.
All files are concentrated under a single directory, whose name is hard coded. So actions such as "reset" are mapped to the deletion of all files under this directory, and iteration actions use file system APIs to traverse the directory.
Data layout
When storing the data, it is stored with a preceding 16-byte metadata header. Metadata includes flags and other parameters for basic validity checks.

Fields are:
- Magic: A constant value, for quick validity checking.
- Metadata size: Size of metadata header.
- Revision: FileSystemStore revision (currently 1).
- User flags: Flags received from user. Currently only write once is dealt with (others are ignored).
Detailed design
FileSystemStore fully implements the KVStore interface over a file system. As such, it uses the FileSystem class interface for file operations.
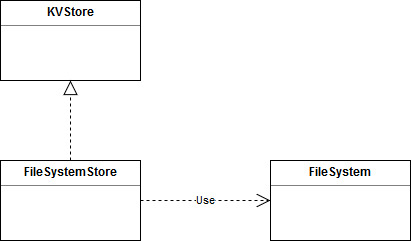
Functionality, as defined by KVStore, includes the following:
- Initialization and reset.
- Core actions: get, set and remove.
- Incremental set actions.
- Iterator actions.
Class header
FileSystemStore has the following header:
class FileSystemStore : KVStore {
public:
FileSystemStore(FileSystem *fs);
virtual ~FileSystemStore();
// Initialization and reset
virtual int init();
virtual int deinit();
virtual int reset();
// Core API
virtual int set(const char *key, const void *buffer, size_t size, uint32_t create_flags);
virtual int get(const char *key, void *buffer, size_t buffer_size, size_t *actual_size = NULL, size_t offset = 0);
virtual int get_info(const char *key, info_t *info);
virtual int remove(const char *key);
// Incremental set API
virtual int set_start(set_handle_t *handle, const char *key, size_t final_data_size, uint32_t create_flags);
virtual int set_add_data(set_handle_t handle, const void *value_data, size_t data_size);
virtual int set_finalize(set_handle_t handle);
// Key iterator
virtual int iterator_open(iterator_t *it, const char *prefix = NULL);
virtual int iterator_next(iterator_t it, char *key, size_t key_size);
virtual int iterator_close(iterator_t it);
private:
Mutex _mutex;
FileSystem *_fs;
bool _is_initialized;
}
Important data structures
// Key metadata
typedef struct {
uint32_t magic;
uint16_t metadata_size;
uint16_t revision;
uint32_t flags;
} key_metadata_t;
// incremental set handle
typedef struct {
char *key;
uint32_t create_flags;
} inc_set_handle_t;
// iterator handle
typedef struct {
void *dir_handle;
char *prefix;
} key_iterator_handle_t;
Initialization and reset
init function
Header:
virtual int init();
Pseudo code:
- If
_is_initialized, return OK. - Create and take
_mutex. - Create the FileSystemStore directory if it doesn't exist.
- Set
_is_initializedto true. - Release
_mutex.deinit function
Header:
virtual int deinit();
Pseudo code:
- If not
_is_initialized, return OK. - Take
_mutex. - Set
_is_initializedto false. - Release
_mutex.
reset function
Header:
virtual int reset();
Pseudo code:
- Take
_mutex. - Delete all files under the FileSystemStore directory.
- Set
_num_keysto 0. - Release
_mutex.
Core APIs
set function
Header:
virtual int set(const char *key, const void *buffer, size_t size, uint32_t create_flags);
Pseudo code:
- If not
_is_initialized, return "not initialized" error. - Call
set_startwith all fields and a localset_handle_tvariable. - Call
set_add_datawithbufferandsize. - Call
set_finalize. - Return OK.
get function
Header:
virtual int get(const char *key, void *buffer, size_t buffer_size, size_t *actual_size = NULL, size_t offset = 0);
Pseudo code:
- If not
_is_initialized, return "not initialized" error. - Take
_mutex. - Using the
statAPI, extract file size. - Open file
keyfor reading to achieve a file handle. - If failed, release
_mutexand return "not found" error. - Read from file into a
key_metadata_tstructure. - Using
sizeAPI, achieve file size. - Seek to
offset+ metadata size. - Set
actual_sizeas the minimum of buffer size and remainder of data. - Read data from file to
buffer, size isactual_size. - Close file.
- Release
_mutex. - Return OK.
get_info function
Header:
virtual int get_info(const char *key, info_t *info);
Pseudo code:
- If not
_is_initialized, return "not initialized" error. - Find file
keyunder the FileSystemStore directory. If not existing, return "not found" error. - Take
_mutex. - Open file
keyfor reading to achieve a file handle. - If failed, release
_mutex, and return "not found" error. - Using
sizeAPI, achieve file size. - Read from file into a
key_metadata_tstructure. - Fill
infostructure with all relevant fields. - Close file.
- Return OK.
remove function
Header:
virtual int remove(const char *key);
Pseudo code:
- If not
_is_initialized, return "not initialized" error. - Take
_mutex. - Open file
keyfor reading, and read data into akey_metadata_tstructure. - If not existing, return "not found error".
- If flag "write once" is preset, return "write once" error.
- Delete file
key. - Release
_mutex. - Return OK.
Incremental set APIs
set_start function
Header:
virtual int set_start(set_handle_t *handle, const char *key, size_t final_data_size, uint32_t create_flags);
Pseudo code:
- Find file
keyunder the FileSystemStore directory. If not existing, increase_num_keysby 1. - Take
_mutex. - Open file for reading, and read data into a
key_metadata_tstructure. - If existing and flag "write once" is preset, return "write once" error.
- Close file.
- Allocate an
inc_set_handle_tstructure intohandle. - Duplicate
keyinhandle. - Update
create_flagsinhandle. - Fill
key_metadata_tstructure with all relevant values (create_flagsfrom handle). - Open file
keyfor writing to achieve a file handle. - Write metadata structure to the file.
- Close file.
set_add_data function
Header:
virtual int set_add_data(set_handle_t handle, const void *value_data, size_t data_size);
Pseudo code:
- Open file
keyfor appending to achieve a file handle. - Write
value_datato the file. - Close file.
set_finalize function
Header:
virtual int set_finalize(set_handle_t handle);
Pseudo code:
- Free
keyinhandleand thenhandle. - Release
_mutex.
Key iterator APIs
iterator_open function
Header:
virtual int iterator_open(iterator_t *it, const char *prefix = NULL);
Pseudo code:
- Take
_mutex. - Allocate a
key_iterator_handle_tstructure intoit. - Duplicate
prefixinto same field in iterator. - Using directory
openAPI, open FileSystemStore directory, and store dir handle in the handle'sdir_handlefield. - Release
_mutex.
iterator_next function
Header:
virtual int iterator_next(iterator_t it, char *key, size_t key_size);
Pseudo code:
- Take
_mutex. - Using direcory
readAPI on handle'sdir_handlefield, read next file in directory. - While not reached end of directory.
- If name matches prefix:
- Copy file name to
key, and return OK.
- Copy file name to
- Using direcory
readAPI on handle'sdir_handlefield, read next file in directory.
- If name matches prefix:
- Return "not found" error.
- Release
_mutex.
iterator_close function
Header:
virtual int iterator_close(iterator_t it);
Pseudo code:
- Using directory
closeAPI ondir_handleclose handle. - Release
prefixfield in iterator and structure allocated atit.
Usage scenarios and examples
Standard usage of the class
The following example code shows standard use of the FileSystemStore class :
Standard usage example
// External file system of LittleFS type. Should be initialized.
extern LittleFileSystem fs;
// Instantiate fsstore with our file system
FileSystemStore fsstore(&fs);
int res;
// Initialize fsstore
res = fsstore.init();
// Add "Key1"
const char *val1 = "Value of key 1";
const char *val2 = "Updated value of key 1";
res = fsstore.set("Key1", val1, sizeof(val1), 0);
// Update value of "Key1"
res = fsstore.set("Key1", val2, sizeof(val2), 0);
uint_8 value[32];
size_t actual_size;
// Get value of "Key1". Value should return the updated value.
res = fsstore.get("Key1", value, sizeof(value), &actual_size);
// Remove "Key1"
res = fsstore.remove("Key1");
// Incremental write, if need to generate large data with a small buffer
const int data_size = 1024;
char buf[8];
KVSTore::set_handle_t handle;
res = fsstore.set_start(&handle, "Key2", data_size, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < data_size / sizeof(buf); i++) {
memset(buf, i, sizeof(buf));
res = fsstore.set_add_data(handle, buf, sizeof(buf));
}
res = fsstore.set_finalize(handle);
// Iterate over all keys starting with "Key"
res = 0;
KVSTore::iterator_t it;
fsstore.iterator_open(&it, "Key*");
char key[KVSTore::KV_MAX_KEY_LENGTH];
while (!res) {
res = fsstore.iterator_next(&it, key, sizeof(key));
}
res = fsstore.iterator_close(&it);
// Deinitialize FileSystemStore
res = fsstore.deinit();
Other information
Open issues
- Need to figure a way to prevent mutex abuse in incremental set APIs.