
 GitBucket
GitBucket
SecureStore in Mbed OS
- SecureStore in Mbed OS
- Introduction
- System architecture and high-level design
- Detailed design
- Usage scenarios and examples
- Other information
Revision history
| Revision | Date | Authors | Mbed OS version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 02 October 2018 | David Saada (@davidsaada) | 5.11+ | Initial revision |
Introduction
Overview and background
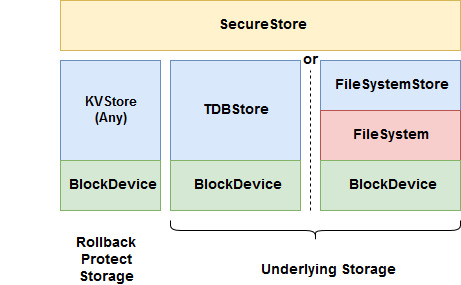
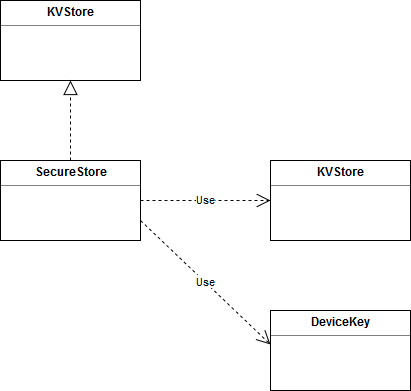
SecureStore is a KVStore based storage solution, providing security features on the stored data, such as encryption, authentication, rollback protection and write once, over an underlying KVStore class. It references an additional KVStore class for storing the rollback protection keys.
Requirements and assumptions
SecureStore assumes that the underlying KVStore instances are instantiated and initialized.
System architecture and high-level design
Design basics
SecureStore is a storage class, derived from KVStore. It adds security features to the underlying key value store. As such, it offers all KVStore APIs, with additional security options (which can be selected using the creation flags at set). These include:
- Encryption: Data is encrypted using the AES-CTR encryption method, with a randomly generated 8-byte IV. Key is derived from Device Key, using the NIST SP 800-108 KDF in counter mode spec, where salt is the key trimmed to 32 bytes, with "ENC" as prefix. Flag here is called "require confidentiality flag".
- Authentication: A 16-byte CMAC is calculated on all stored data (including metadata) and stored at the end of the record. When reading the record, calculated CMAC is compared with the stored one. In the case of encryption, CMAC is calculated on the encrypted data. The key used for generating the CMAC is derived from Device Key, where salt is the key trimmed to 32 bytes, with "AUTH" as prefix. Flag here is called "Require integrity flag".
- Rollback protection: (Requires authentication) CMAC is stored in a designated rollback protected storage (also of KVStore type) and compared to when reading the data under the same KVStore key. A missing or different key in the rollback protected storage results in an error. The flag here is called "Require replay protection flag".
- Write once: Key can only be stored once and can't be removed. The flag here is called "Write once flag".
Data layout
When storing the data, it is stored with a preceding metadata header. Metadata includes flags and security related parameters, such as IV. The CMAC, calculated for authentication, is stored at the end of the data as it is calculated on the fly, so it can't be stored with the metadata.

Fields are:
- Metadata size: Size of metadata header.
- Revision: SecureStore revision (currently 1).
- Data size: Size of user data.
- Flags: User flags.
- IV: Random generated IV.
- Pad: Pad data to a multiple of 16 bytes (due to encryption).
- CMAC: CMAC calculated on key, metadata and data.
Basic implementation concepts
Because the code can't construct a single buffer to store all data (including metadata and possibly encrypted data) in one shot, setting the data occurs in chunks, using the incremental set APIs. Get uses the offset argument to extract metadata, data and CMAC separately.
Rollback protection (RBP) keys are stored in the designated rollback protection storage, which is also of KVStore type. RBP keys are the same as the SecureStore keys.
Detailed design
Functionality, as defined by KVStore, includes the following:
- Initialization and reset.
- Core actions: get, set and remove.
- Incremental set actions.
- Iterator actions.
Class header
SecureStore has the following header:
class SecureStore : KVStore {
public:
SecureStore(KVStore *underlying_kv, KVStore *rbp_kv);
virtual ~SecureStore();
// Initialization and formatting
virtual int init();
virtual int deinit();
virtual int reset();
// Core API
virtual int set(const char *key, const void *buffer, size_t size, uint32_t create_flags);
virtual int get(const char *key, void *buffer, size_t buffer_size, size_t *actual_size = NULL, size_t offset = 0);
virtual int get_info(const char *key, info_t *info);
virtual int remove(const char *key);
// Incremental set API
virtual int set_start(set_handle_t *handle, const char *key, size_t final_data_size, uint32_t create_flags);
virtual int set_add_data(set_handle_t handle, const void *value_data, size_t data_size);
virtual int set_finalize(set_handle_t handle);
// Key iterator
virtual int iterator_open(iterator_t *it, const char *prefix = NULL);
virtual int iterator_next(iterator_t it, char *key, size_t key_size);
virtual int iterator_close(iterator_t it);
private:
Mutex _mutex;
KVStore *_underlying_kv;
KVStore *_rbp_kv;
void *_entropy;
uint8_t *_scratch_buf;
}
Important data structures
// Record header
typedef struct {
uint16_t metadata_size;
uint16_t revision;
uint32_t data_size;
uint32_t create_flags;
uint8_t iv[8];
} record_metadata_t;
// incremental set handle
typedef struct {
record_metadata_t metadata;
bd_size_t offset;
char *key;
void *encrypt_handle;
void *auth_handle;
KVStore::set_handle_t underlying_handle;
} inc_set_handle_t;
// iterator handle
typedef struct {
KVStore::iterator_t underlying_it;
} key_iterator_handle_t;
Initialization and reset
init function
Header:
virtual int init();
Pseudo code:
- if
_is_initialized, return OK. - Take
_mutex. - Initialize
_entropywith TLS entropy APIs. - Using
DeviceKeyAPIs, get the device key. - Allocate
_scratch_bufas a 32 byte array. - Set
_is_initializedto true. - Release
_mutex.deinit function
Header:
virtual int deinit();
Pseudo code:
- if not
_is_initialized, return OK. - Take
_mutex. - Deinitialize
_entropy. - Deallocate
_scratch_buf. - Release
_mutex.
reset function
Header:
virtual int reset();
Pseudo code:
- Take
_mutex. - Call
_underlying_kvresetAPI. - Call
_rbp_kvresetAPI. - Release
_mutex.
Core APIs
set function
Header:
virtual int set(const char *key, const void *buffer, size_t size, uint32_t create_flags);
Pseudo code:
- Call
set_startwith all fields and a localset_handle_tvariable. - Call
set_add_datawithbufferandsize. - Call
set_finalize. - Return OK.
get function
Header:
virtual int get(const char *key, void *buffer, size_t buffer_size, size_t *actual_size = NULL, size_t offset = 0);
Pseudo code:
- if not
_is_initializedreturn error. - Take
_mutex. - Call
_underlying_kvgetAPI withmetadatasize into ametadatalocal structure. - If failure:
- If rollback protection flag set:
- Call
_rbp_kvgetAPI on a localrbp_cmacvariable, key iskey, size 16. - If no error, return "RBP authentication" error.
- Call
- Return "Key not found error".
- If rollback protection flag set:
- If authentication flag set:
- Derive a key from device key and
key. - Allocate and initialize
auth_handleCMAC calculation local handle with derived key. - Using
auth_handlehandle, calculate CMAC onkeyandmetadata.
- Derive a key from device key and
- If encrypt flag set:
- Derive a key from device key and
key. - Allocate and initialize a local
enc_handleAES-CTR local handle with derived key andivfield.
- Derive a key from device key and
- Set
data_sizelocal variable to data size in metadata. - Set
actual_sizeto the minimum ofbuffer_sizeanddata_size. - Set
current_offsetto 0. - While
data_size> 0:- If
current_offsetbetweenoffsetandactual_size.- Set
dest_buftobufferandchunk_sizetoactual_size.
- Set
- Else:
- Set
dest_bufto_scratch_bufandchunk_sizetoactual_size.
- Set
- Call
_underlying_kvgetAPI withdest_bufandchunk_size. - If authentication flag set, calculate CMAC on
dest_buf, using_auth_handlehandle. - If encrypt flag set, decrypt
dest_buf(in place) using_enc_handlehandle. - Decrement
data_sizebychunk_size.
- If
- Call
_underlying_kvgetAPI with on a localread_cmacvariable, size 16. - Generate CMAC on local
cmacvariable . - Using
mbedtls_ssl_safer_memcmpfunction, compareread_cmacwithcmac. Return "data corrupt error" if no match. - If rollback protection flag set:
- Call
_rbp_kvgetAPI on a localrbp_cmacvariable, key iskey, size 16. - If
rbp_cmacdoesn't matchcmac, clearbufferand return "RBP authentication" error.
- Call
- Deinitialize and free
auth_handleandenc_handle. - Release
_mutex. - Return OK.
get_info function
Header:
virtual int get_info(const char *key, info_t *info);
Pseudo code:
- If not
_is_initialized, return error. - Call
getAPI withkeyand 0 inbuffer_sizeparameter. - If failed, return error code.
- Call
_underlying_kvgetAPI withmetadatasize andkey. - Fill fields in
infoaccording tometadata. - Return OK.
remove function
Header:
virtual int remove(const char *key);
Pseudo code:
- If not
_is_initialized, return error. - Take
_mutex. - Call
_underlying_kvgetAPI withmetadatasize andkey. - If not found, return "Not found" error.
- If write once flag set, return "Already exists" error.
- Call
_underlying_kvremoveAPI withkey. - If rollback protect flag set, call
_rbp_kvremoveAPI withkeyas key. - Return OK.
Incremental set APIs
set_start function
Header:
virtual int set_start(set_handle_t *handle, const char *key, size_t final_data_size, uint32_t create_flags);
Pseudo code:
- Take
_mutex. - Allocate an
inc_set_handle_tand assign in handle. - If flags include write once flag:
- Call
_underlying_kvget_infoAPI. - If key exists, return "already exists" error.
- Call
_rbp_kvgetAPI withkeyas key. If key exists, return "already exists" error.
- Call
- If encrypt flag set:
- Derive a key from device key and
keyas salt (trimmed to 32 bytes with "ENC" as prefix). - Using TLS entropy function on
_entropyhandle, randomly generateivfield. - Allocate and initialize
enc_handleAES-CTR handle field with derived key andivfield.
- Derive a key from device key and
- Fill all available fields in
metadata. - If authentication flag set:
- Derive a key from device key and
keyas salt (trimmed to 32 bytes with "AUTH" as prefix). - Allocate and initialize
auth_handleCMAC calculation handle field with derived key. - Using
auth_handlehandle, calculate CMAC onkeyandmetadata.
- Derive a key from device key and
- Call
_underlying_kvset_startAPI. - Call
_underlying_kvset_add_dataAPI withmetadatafield. - Return OK.
set_add_data function
Header:
virtual int set_add_data(set_handle_t handle, const void *value_data, size_t data_size);
Pseudo code:
- If
offset+data_size> data size in handle, return error. - If flags include encryption:
- Iterate over
value_datafield in chunks of_scratch_bufsize.- Using
enc_handlehandle field, encrypt chunk into_scratch_buf. - If authentication flag set, using
auth_handlehandle field, update CMAC of_scratch_buf. - Call
_underlying_kvset_add_dataAPI with_scratch_buf.
- Using
- Iterate over
- Else:
- If authentication flag set, using
auth_handlehandle field, update CMAC ofvalue_data. - Call
_underlying_kvset_add_dataAPI withvalue_data.
- If authentication flag set, using
- Update
offsetfield in handle. - Return OK.
set_finalize function
Header:
virtual int set_finalize(set_handle_t handle);
Pseudo code:
- Initialize a local
cmac16-byte array to 0. - If authentication flag set, using
auth_handlehandle field, generatecmac. - Call
_underlying_kvset_add_dataAPI withcmac. - Call
_underlying_kvset_finalize. - If rollback protect flag set, call
_rbp_kvsetAPI withkeyas key andcmacas data. - Deinitialize and free
auth_handleandenc_handle. - Free
handle. - Release
_mutex. - Return OK.
Key iterator APIs
iterator_open function
Header:
virtual int iterator_open(iterator_t *it, const char *prefix = NULL);
Pseudo code:
- Allocate a
key_iterator_handle_tstructure intoit. - Take
_mutex. - Call
_underlying_kviterator_openwithunderlying_itfield. - Release
_mutex. - Return OK.
iterator_next function
Header:
virtual int iterator_next(iterator_t it, char *key, size_t key_size);
Pseudo code:
- Take
_mutex. - Call
_underlying_kviterator_nextwithunderlying_itfield. - Release
_mutex. - Return OK.
iterator_close function
Header:
virtual int iterator_close(iterator_t it);
Pseudo code:
- Take
_mutex. - Call
_underlying_kviterator_closewithunderlying_itfield. - Release
_mutex. - Deallocate
it. - Return OK.
Usage scenarios and examples
Standard use of the class
The following example code shows standard use of the SecureStore class:
Standard usage example
// Underlying key value store - here TDBStore (should be instantiated and initialized)
extern TDBStore tdbstore;
// Rollback protect store - also of TDBStore type (should be instantiated and initialized)
extern TDBStore rbp_tdbstore;
// Instantiate SecureStore with tdbstore as underlying key value store and rbp_tdbstore as RBP storage
SecureStore secure_store(&tdbstore, &rbp_tdbstore);
int res;
// Initialize secure_store
res = secure_store.init();
const char *val1 = "Value of key 1";
const char *val2 = "Updated value of key 1";
// Add "Key1" with encryption and authentication flags
res = secure_store.set("Key1", val1, sizeof(val1), KVSTore::REQUIRE_CONFIDENTIALITY_FLAG | KVSTore::REQUIRE_INTEGRITY_FLAG);
// Update value of "Key1" (flags must be the same per key)
res = secure_store.set("Key1", val2, sizeof(val2), KVSTore::REQUIRE_CONFIDENTIALITY_FLAG | KVSTore::REQUIRE_INTEGRITY_FLAG);
uint_8 value[32];
size_t actual_size;
// Get value of "Key1". Value should return the updated value.
res = secure_store.get("Key1", value, sizeof(value), &actual_size);
// Remove "Key1"
res = secure_store.remove("Key1");
// Incremental write, if need to generate large data with a small buffer
const int data_size = 1024;
char buf[8];
KVSTore::set_handle_t handle;
res = secure_store.set_start(&handle, "Key2", data_size, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < data_size / sizeof(buf); i++) {
memset(buf, i, sizeof(buf));
res = secure_store.set_add_data(handle, buf, sizeof(buf));
}
res = secure_store.set_finalize(handle);
// Iterate over all keys starting with "Key"
res = 0;
KVSTore::iterator_t it;
secure_store.iterator_open(&it, "Key*");
char key[KVSTore::KV_MAX_KEY_LENGTH];
while (!res) {
res = secure_store.iterator_next(&it, key, sizeof(key)e);
}
res = secure_store.iterator_close(&it);
// Deinitialize SecureStore
res = secure_store.deinit();
Other information
Open issues
- Need to figure a way to prevent mutex abuse in incremental set APIs.